Music in the Classical Era
 White House built 1792-1800
White House built 1792-1800
The classical era of music spanned from the mid-18th century to the early 19th century and is an important period in the history of Western classical music. Composers like Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, Joseph Haydn, Ludwig van Beethoven, and Franz Schubert were popular. The improvisational and highly ornamented style of the Baroque era was replaced by a simpler, lighter sound, where composers clearly specified which ornaments and dynamics they wanted to use and preferred a clean sound with a memorable melody and distinct musical form.
During the classical era, there was a shift in architecture, literature, and art towards emulating Classical antiquity, especially Classical Greece. Buildings were symmetrical, strong, and used many columns. These preferences can also be found in the musical forms of the classical era.
During the classical era, there was a shift in architecture, literature, and art towards emulating Classical antiquity, especially Classical Greece. Buildings were symmetrical, strong, and used many columns. These preferences can also be found in the musical forms of the classical era.
Life in the Classical Era
The classical era has been known as the Age of Enlightenment or the Age of Reason. The American (1765-1783) and French Revolutions (1789-1799) took place during this time. As the church and monarchies began to lose their power, a middle class rose to prominence. Middle class valued education and reason. The major philosophy of the day was that logic and reason should govern all activities, including the arts. The middle class also wanted to be entertained, so there was a rise in comic operas and secular music. New inventions like the steam engine greatly influenced society. The Industrial Revolution (1760-1840) made factory made products on assembly lines popular.
Classical Music Terms to Know
Homophonic
During the classical era, music became more homophonic in texture. Homophonic means there was a main melody on top of a harmonic progression. This was different than the polyphonic texture (two or more melodies sounding at once) of the Baroque era.
Alberti Bass
Mozart popularized the alberti bass in his keyboard music. Alberti Bass is a left hand accompaniment using a broken chord in a 1-5-3-5 order.
Cadences
During the classical era, there was an emphasis on music with strong cadences. Cadences are harmonic endings of phrases in Western music. An authentic cadence uses a IV-V7-I harmonic progression. Half cadences (IV-V) and deceptive cadences (IV-V-VI) are also common cadences in Western music and were often used at this time.
During the classical era, music became more homophonic in texture. Homophonic means there was a main melody on top of a harmonic progression. This was different than the polyphonic texture (two or more melodies sounding at once) of the Baroque era.
Alberti Bass
Mozart popularized the alberti bass in his keyboard music. Alberti Bass is a left hand accompaniment using a broken chord in a 1-5-3-5 order.
Cadences
During the classical era, there was an emphasis on music with strong cadences. Cadences are harmonic endings of phrases in Western music. An authentic cadence uses a IV-V7-I harmonic progression. Half cadences (IV-V) and deceptive cadences (IV-V-VI) are also common cadences in Western music and were often used at this time.
What were popular classical music forms?
|
Sonata
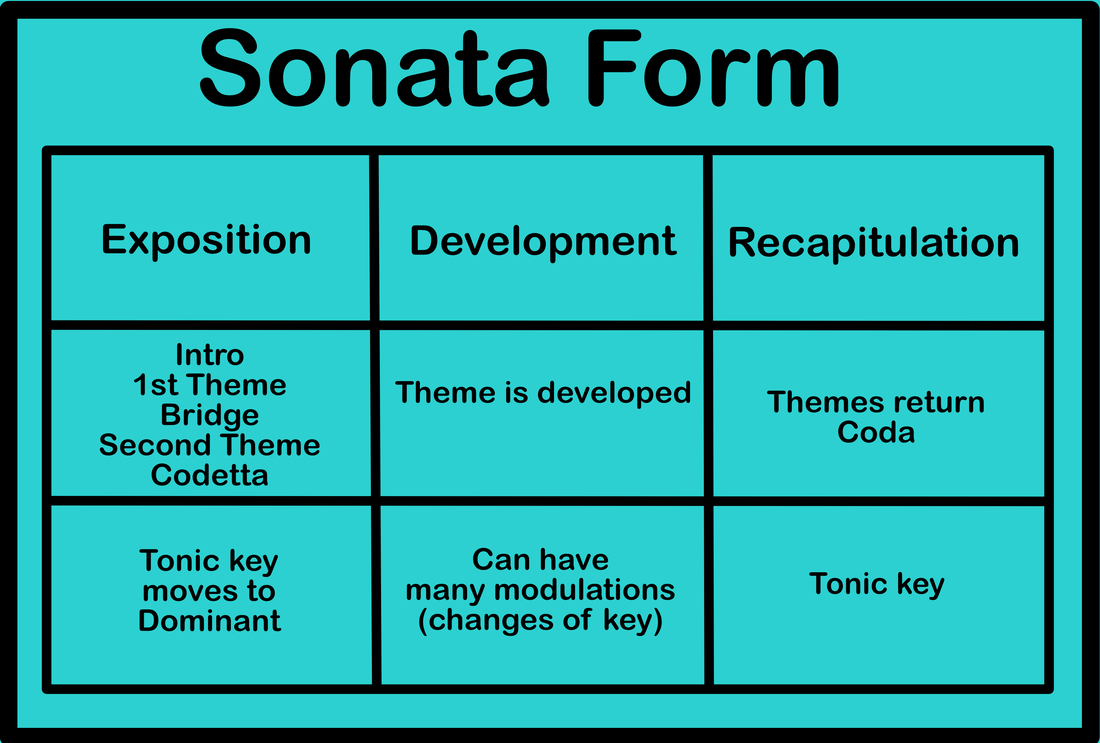
There were many new forms of instrumental music during the classical era. One form of classical music was the sonata. Sonata form has three parts: exposition, development, and recapitulation. Sometimes there was even an introduction and a "coda" or tail end section. In sonata form, the key changes from the original key and then returns back to the key it started in. There is also a main theme that is developed throughout the piece. Symphony The symphony was a form of music composed for full orchestra. It had four parts called movements. The first movement was typically in Sonata form and in a key called the tonic which was the home key. The second movement could be in sonata form, theme and variation, or ABA and was very slow and melodic. The second movement also changed to a different key. The third movement moved back to the home key and was usually a minuet and trio, a dance, or scherzo. This movement could be a faster tempo. The fourth movement was the fastest and most exciting movement of the symphony. This movement was in the tonic key and was usually a sonata or sonata-rondo form. Concerto Another form of classical music is the concerto. In Italian, concerto means “concert or harmony.” In this form, there is a soloist and an orchestra or other ensemble. The soloist is really good and the music is very hard to play, displaying the musician’s virtuosity. The orchestra and soloist go back and forth and create a harmony together. |
Critical Thinking Questions
- How are a symphony, sonata, and concerto different from each other?
- What music characteristics define the classical era?
| sonata_form_worksheet.pdf | |
| File Size: | 81 kb |
| File Type: | |